The Impact of Extended Reality (XR) Solutions on Business Transformation
- Oliver Richard
In an era of rapid technological advancements, Extended Reality (XR) stands out as a game-changing force that merges digital and physical environments. But what is Extended Reality? XR is a collective term encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). These immersive technologies bridge the gap between the real and virtual worlds, redefining how we learn, work, socialize, and engage with content. With the advent of Extended Reality solutions powered by 5G and AI, industries such as education, healthcare, and retail are experiencing groundbreaking transformations.
Understanding the Core Components of XR
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encapsulates various immersive technologies transforming how we interact with digital and physical environments. It relies on three core components: Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR). Each offers unique capabilities, catering to a range of applications across industries.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Full Immersion in Digital Realms
VR creates fully immersive experiences with tools like advanced VR headsets. In platforms like Oracle Learning Cloud, virtual and extended reality are revolutionizing corporate training and skill development through lifelike simulations.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Enhancing the Real World
AR enhances the real world with interactive overlays, enabling extended reality in business applications such as virtual product trials and immersive customer engagement.
- Mixed Reality (MR): The Best of Both Worlds
MR seamlessly combines physical and digital worlds, unlocking potential in fields like education and manufacturing. It’s a key area for extended reality companies driving innovation.
How Industries Shape and Leverage XR?
The evolution of Extended Reality (XR) is shaped significantly by the synergy of industries like IT, social media, and online communities. These sectors not only drive its adoption but also redefine its potential in practical applications.

- IT Sector – The Backbone of XR Infrastructure
The IT sector plays a pivotal role in developing the underlying architecture for XR. By ensuring robust, cloud-based XR solutions, IT firms provide scalable platforms for seamless integration. From AI-powered XR experiences to IoT-enabled XR systems, the IT industry continues to enable innovations like digital twins in XR and real-time virtual collaboration. - Social Media – Augmented Engagement Through AR
Social media platforms integrate augmented retail shopping and interactive filters, leveraging AR tools to create unique experiences. Features like virtual try-ons and immersive storytelling redefine user engagement, highlighting the role of AR and VR trends 2024 in personalizing content. - Online Communities – Democratizing Access to XR
Online communities enable collaboration and creativity, fostering widespread access to XR technology. By sharing interactive 3D experiences and ideas, they democratize innovation, empowering developers and users to contribute to the growth of future immersive technologies.
The Role of Technological Advancements
The trajectory of XR owes much to rapid progress in hardware and software.
- Ergonomic and Lightweight Hardware
Modern headsets offer AI-driven virtual experiences, making XR devices more accessible and user-friendly. - 5G and IoT Integration
5G networks enhance connectivity, enabling real-time virtual collaboration and smooth performance of cloud-based XR solutions. - AI Enhancements
AI elevates XR by personalizing interactive 3D experiences and ensuring dynamic, context-sensitive interactions.
Real-World Applications of XR
Extended Reality (XR) is reshaping industries by creating immersive, interactive experiences powered by AI-driven XR solutions and advancements in 5G and cloud-based XR systems.

- Education and Training
Through Oracle Learning Cloud, XR facilitates personalized learning and immersive virtual environments. In medicine, XR simulates surgeries for skill-building without real-world risks, while aviation training leverages AI-powered XR experiences for precision and safety. These advancements enable a hands-on approach, enhancing knowledge retention and skill development. - Healthcare
In healthcare, extended reality solutions empowers professionals with interactive 3D experiences and precise tools. Surgeons use VR to plan complex procedures, while therapeutic VR applications aid in pain management and mental health treatments. AI-enhanced XR systems provide real-time data overlays, boosting diagnostic accuracy and patient care. - Retail
Retail is adopting extended reality in business, offering augmented shopping experiences. AR applications, such as virtual furniture placement or cosmetic trials, enhance decision-making. This immersive approach improves customer satisfaction, blending the physical and digital shopping experience seamlessly. - Gaming and Entertainment
XR is redefining entertainment through immersive storytelling and dynamic gaming environments. Players can explore virtual worlds, interact with AI-driven virtual experiences, and enjoy cinematic visuals like never before. XR’s role in the future of immersive technology ensures its dominance in crafting next-gen entertainment experiences.
As industries continue to innovate with IoT-integrated XR systems and cloud-based XR solutions, the practical applications of XR will expand further, driving efficiency, creativity, and user engagement across multiple domains.
Challenges of XR Development
While XR technology offers numerous benefits, its development presents several challenges from high hardware costs to data privacy concerns. For extended reality companies, overcoming these barriers is crucial to achieving widespread adoption.
- High Costs of Hardware
The high cost of XR hardware and maintenance limits accessibility, making it challenging for users and businesses to adopt. - Platform Compatibility
Ensuring seamless XR performance across different devices and operating systems requires extensive testing and optimization, often complicating integration into existing systems. - Data Privacy Concerns
Personalized XR experiences raise privacy concerns over user data, requiring secure handling to maintain trust, especially in sectors like healthcare and retail. - User Experience & Motion Sickness
Ensuring comfort in XR experiences is challenging, as motion sickness and discomfort from prolonged use can affect some users. - Scalability and Maintenance
As XR technologies evolve, businesses face challenges in scaling and maintaining systems, often struggling to integrate them into existing IT infrastructure.
The Explosive Growth and Impact of XR
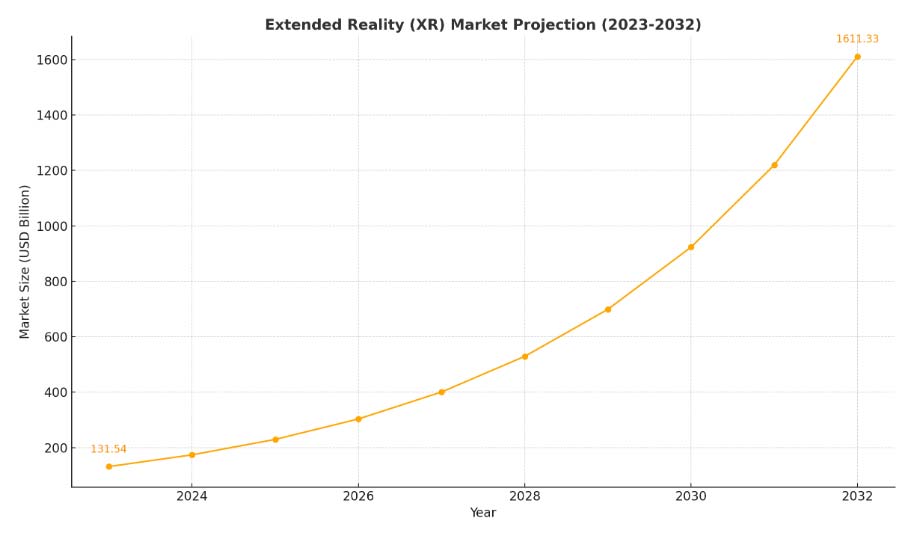
XR is rapidly reshaping industries, fueled by technological advancements and growing business interest. A study by XR Today reveals 41% of companies focus on XR R&D, while 56% see Meta as a key partner. The global XR market, valued at $131.54 billion in 2023, is projected to reach $1,706.96 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 32.1%, with VR driving growth in gaming and entertainment, according to Fortune Business Insights.
According to Axis, another major trend is the integration of Generative AI with XR, which will enable highly personalized experiences. AI-driven XR environments will adapt in real time based on user preferences, enhancing engagement and interactivity. This synergy between AI and XR is expected to redefine how we interact with virtual spaces, making them more dynamic and realistic.
Discover XR Solutions with Innovature Labs
Extended Reality is transforming industries, bridging the physical and digital, and offering endless possibilities. From interactive 3D experiences to AI-driven virtual interactions, XR is reshaping how we live, learn, and connect.
At Innovature Labs, we provide cutting-edge, cloud-based extended reality solutions tailored to your unique business needs. Our expertise spans virtual and extended reality applications, helping companies integrate XR into Oracle Learning Cloud and beyond.











